Cache Reserve (beta)
Cache Reserve is a large, persistent data store implemented on top of R2. By pushing a single button in the dashboard, all of your website’s cacheable content will be written to Cache Reserve. In the same way that Tiered Cache builds a hierarchy of caches between your visitors and your origin, Cache Reserve serves as the ultimate upper-tier cache that will reserve storage space for your assets for as long as you want. This ensures that your content is served from cache longer, shielding your origin from unneeded egress fees.
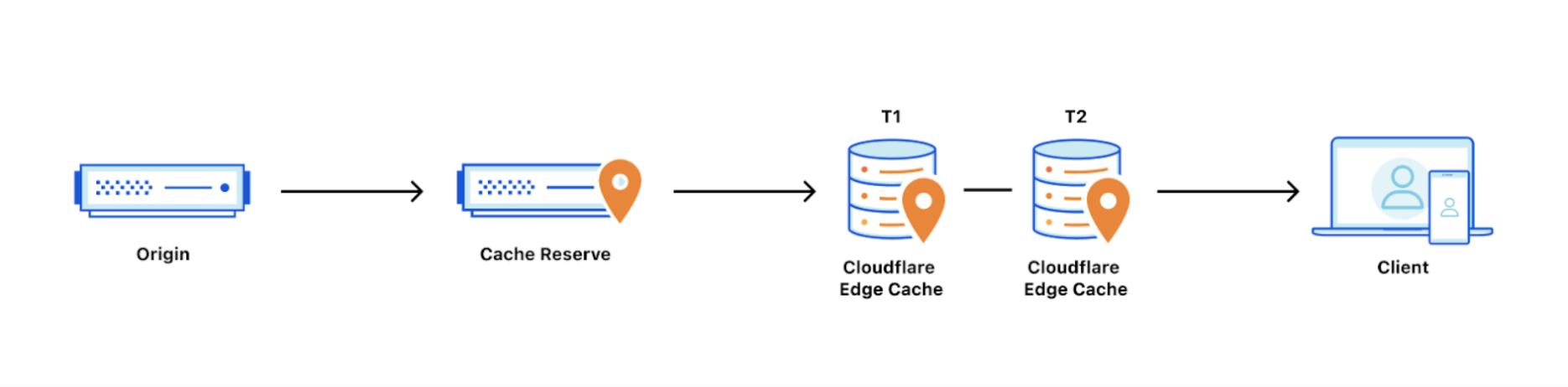
How long content in Cache Reserve will be considered “fresh” is determined by edge cache TTL setting or Cache-Control headers at your origin, if edge cache TTL is not set. After the retention period expires, Cloudflare will revalidate the asset when a subsequent request arrives in Cache Reserve for the asset. This is the same behavior as in Cloudflare’s regular CDN.
The retention period of an asset is how long we will keep the asset in Cache Reserve before marking it for eviction. If an asset is not requested within the retention period, it will be evicted from Cache Reserve. Every access will extend the retention period of the asset by exactly one period.
Cache Reserve is a usage-based product and pricing is detailed below.
Enable Cache Reserve
You can enable Cache Reserve from the dashboard or via API. In both situations, you need a paid Cache Reserve Plan.
To enable Cache Reserve through the dashboard:
- Log in to the Cloudflare dashboard and select a domain.
- Navigate to Caching.
- Enable Cache Reserve.
If you are an Enterprise customer and are interested in Cache Reserve, contact your account team to get help with your configuration.
Documentation for enabling Cache Reserve via API, is forthcoming.
Limits
- Cache Reserve file limits are the same as standard CDN cache limits (up to R2 limits).
- Origin Range requests are not supported at this time from Cache Reserve.
- Vary for Images is currently not compatible with Cache Reserve.
Pricing
Cache Reserve charges based on the total volume of data stored, along with two classes of operations on that data:
- Class A operations which are more expensive and tend to mutate state.
- Class B operations which tend to read existing state.
Cache Reserve pricing
| Rates | |
|---|---|
| Storage | $0.015 / GB-month |
| Class A Operations (writes) | $4.50 / million requests |
| Class B Operations (reads) | $0.36 / million requests |
Storage usage
Storage is billed using gigabyte-month (GB-month) as the billing metric. A GB-month is calculated by recording total bytes stored for the duration of the month.
For example:
- Storing 1 GB for 30 days will be charged as 1 GB-month.
- Storing 2 GB for 15 days will be charged as 1 GB-month.
Operations
Operations are performed by Cache Reserve on behalf of the user to write data from the origin to cache reserve and to pass that data downstream to other parts of Cloudflare’s network. These operations are managed internally by Cloudflare.
Class A operations (writes)
Class A operations are performed based on cache misses from Cloudflare’s CDN. When a request cannot be served from cache, it will be fetched from the origin and written to cache reserve as well as our edge caches on the way back to the visitor.
Class B operations (reads)
Class B operations are performed when data needs to be fetched from Cache Reserve to respond to a miss in the edge cache.
Operations billing examples
- 1,000,000 writes in a month will be charged $4.50.
- 1,000,000 reads in a month will be charged $0.36.
- 2,999,000 writes will be charged $9.00.
Free operations
Free operations include purging assets.
Cache Reserve will respect Cache-Control and CDN-Cache-Control headers.
Cache Reserve will also be purged along with edge cache when you send a purge by URL request. Other purge methods such as purge by tag or prefix will invalidate the asset in Cache Reserve, but assets purged this way will still incur storage costs until they expire.
While Cache Reserve does require a paid plan, users can continue to use Cloudflare’s CDN (without Cache Reserve) for free.
Tips and best practices
Cache Reserve should be used with Tiered Cache enabled. Cache Reserve is designed for use with Tiered Cache enabled for maximum origin shielding. Using Cache Reserve without Tiered Cache may result in higher storage operation costs. Enabling Cache Reserve via the Cloudflare dashboard will check and provide a warning if you try to use Cache Reserve without Tiered Cache enabled.