Cisco Viptela SD-WAN
Cloudflare partners with Cisco’s 8000k router SD-WAN solution to provide users with an integrated solution. The Viptela appliances (physical and virtual) manage subnets associated with branch offices and cloud instances. Anycast Tunnels – GRE and IPsec – are set up between these appliances and Cloudflare to securely route Internet-bound traffic. This tutorial describes how to configure the Cisco 8000k router in the SD-WAN mode for north-south (Internet-bound) use cases.
Prerequisites
Before setting up a connection between Cisco Viptela and Cloudflare, you must have:
- Purchased Magic WAN and Secure Web Gateway.
- Cloudflare provision Magic WAN and Secure Web Gateway.
- Received two Cloudflare tunnel endpoints (Anycast IP address) assigned to Magic WAN.
- Cisco 8000k SD-WAN appliances (physical or virtual). This ensures specific Internet-bound traffic from the sites' private networks is routed over the Anycast GRE tunnels to Secure Web Gateway to enforce a user’s specific web access policies.
- A static IP pair to use with the tunnel endpoints. The static IPs should be /31 addresses separate from the IPs used in the subnet deployment. The software version used on Cisco was
20.6.2/17.6.2.
Example scenario
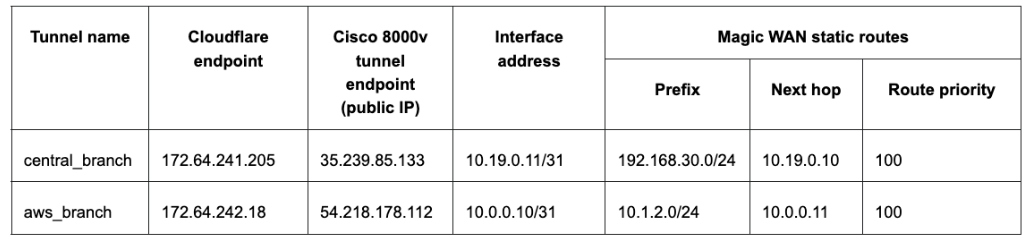
For the purpose of this tutorial, the integration will refer to a scenario with one branch office with subnets. The central branch office has a 192.168.30.0/24 network with the SD-WAN appliance terminating the Anycast GRE tunnel. The central branch office has a 192.168.30.0/24 network with the SD-WAN appliance terminating the Anycast IPsec tunnel.GRE tunnel configuration
IPsec tunnel configuration
1. Create a SIG template on Cisco vManage
Cisco vManage is Cisco’s SD-WAN management tool that is used to manage all the SD-WAN appliances in branch offices. For this example scenario, a non-default template for To create a Secure Internet Gateway (SIG) using vManage: Transport & Management VPN settings Basic Information settings When creating the Feature Template, you can choose values that apply globally or that are device specific. For example, the Tunnel Source IP Address, Interface Name and fields from Update Tunnel are device specific and should be chosen accordingly. For this example scenario, a non-default template for SIG-Branch-IPsec-Template was created. To create a Secure Internet Gateway (SIG) using vManage:GRE tunnel configuration
SIG-Branch was created.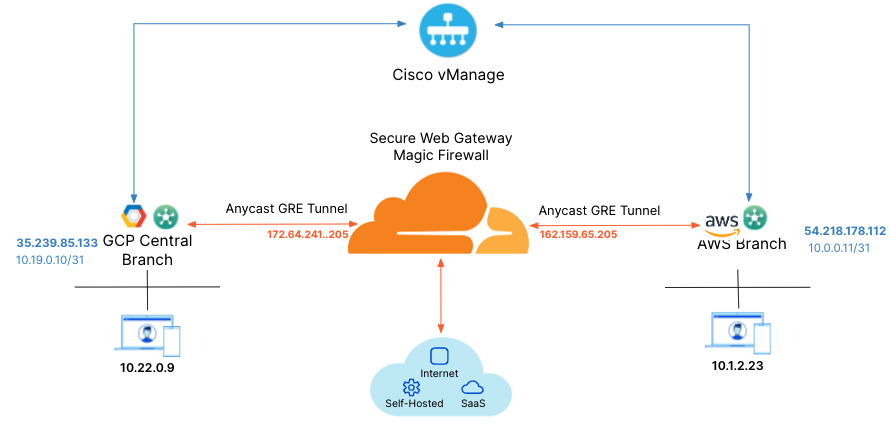
Setting Type/Detail Global Template Factory_Default_Global_CISCO_Template Cisco Banner Factory_Default_Retail_Banner Policy Branch-Local-Policy Setting Type/Detail Cisco VPN 0 GCP-Branch-VPN0 Cisco Secure Internet Gateway Branch-SIG-GRE-Template Cisco VPN Interface Ethernet GCP-Branch-Public-Internet-TLOC Cisco VPN Interface Ethernet GCP-VPN0-Interface Cisco VPN 512 Default_AWS_TGW_CSR_VPN512_V01 Setting Type/Detail Cisco System Default_BootStrap_Cisco_System_Template Cisco Loging Default_Logging_Cisco_V01 Cisco AAA AWS-Branch-AAA-Template Cisco BFD Default_BFD_Cisco-V01 Cisco OMP Default_AWS_TGW_CSR_OMP_IPv46_… Cisco Security Default_Security_Cisco_V01 IPsec tunnel configuration
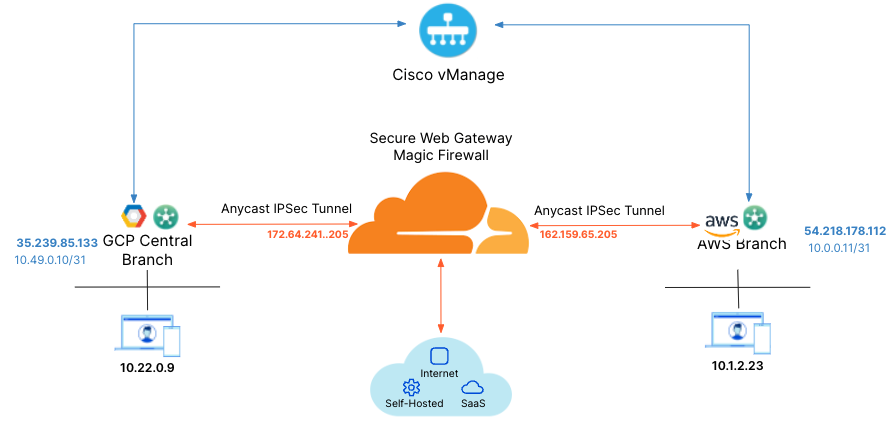
Setting Type/Detail Tunnel Type IPsec Interface Name (1..255) Global Description IP Tunnel Source IP Address Device-Specific IPv4 addresses Device-Specific Tunnel Route-via Interface Device-Specific Tunnel Destination IP Address/FQDN(Ipsec) Device-Specific Preshared key Device-Specific IPsec Rekey Interval (under advanced options) Default IPsec Replay Window Default IPSec Cipher Suite Global (AES 256 CBC SHA 256) Perfect Forward Secrecy Global (Group-14 2048-bit modulus)
2. (IPsec only) Create a non-default feature template
For compatibility, you will need to disable replay protection, which is not an option through the templates, by creating a CLI template in addition to the feature template created in the previous step.
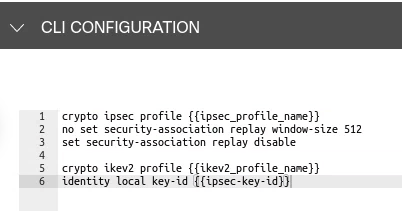
In the image above, replay is disabled and the local key-id is set to a variable so that a Cloudflare tunnel ID with the format xxxxxx_YYYYYYY can be added.
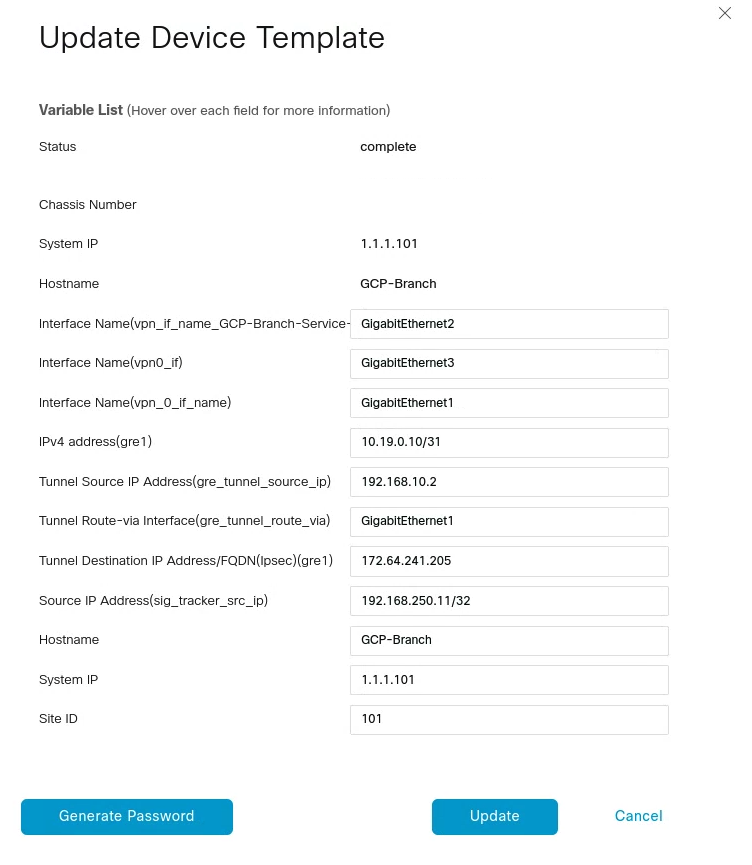
3. Create tunnels in vManage
GRE tunnel configuration
From vManage, click Configuration > Templates. You should see the newly created template where you will update the device values.
Because the template was created to add GRE tunnels, you only need to update the device values. Note that VPN0 is the default, and the WAN interface used to build the tunnel must be part of VPN0.
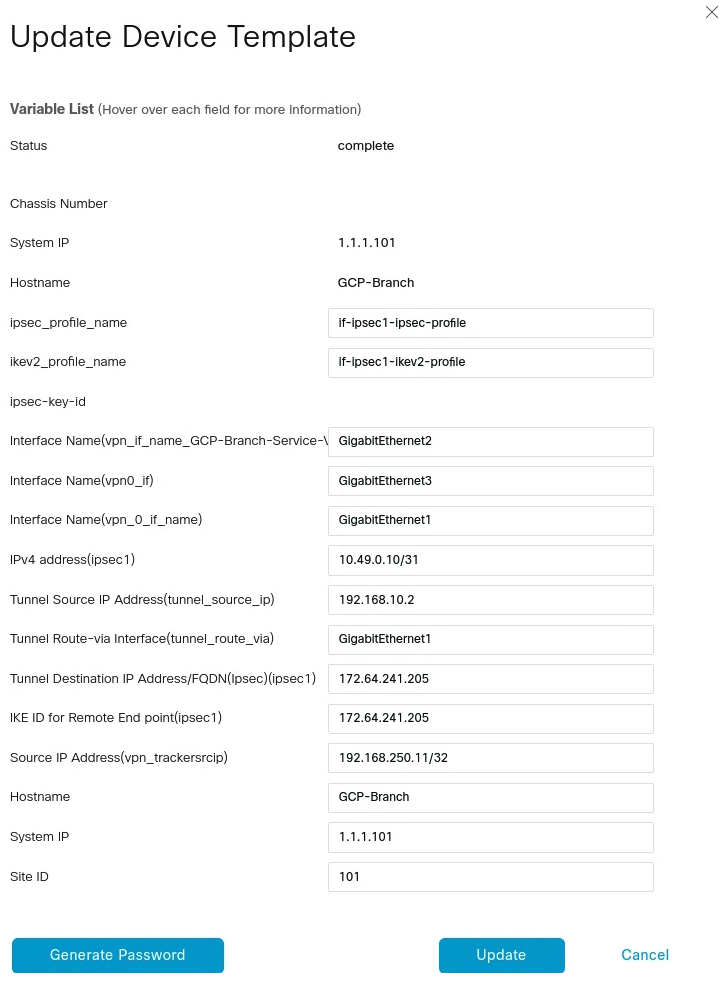
IPsec tunnel configuration
From vManage, click Configuration > Templates. You should see the newly created template where you will update the device values.
In the example below, the template is the GCP-Branch-Template. Note that VPN0 is the default, and the WAN interface used to build the tunnel needs to be part of VPN0.
4. Create tunnels in Cloudflare
GRE tunnel configuration
Refer to Configure tunnel endpoints for more information on creating a GRE tunnel.
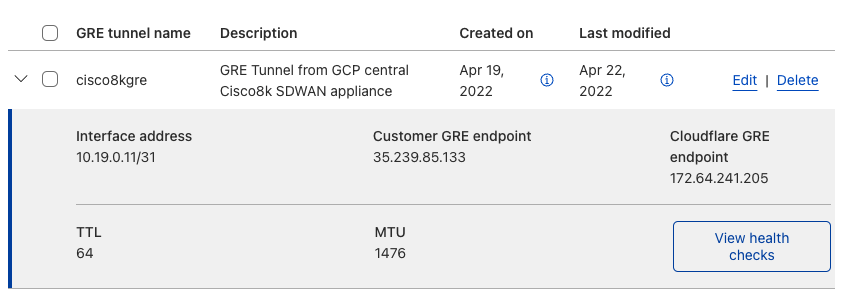
IPsec tunnel configuration
For additional information on creating IPsec tunnels, refer to API documentation for IPsec tunnels.
X-Auth-Email: Your Cloudflare email IDX-Auth-Key: Seen in the URL (dash.cloudflare.com//….) Account key: Global API token in Cloudflare dashboard
Test new IPsec tunnel creation
Request
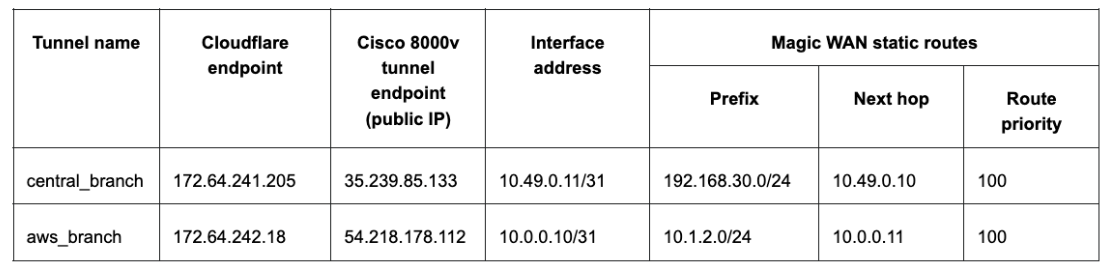
curl -X POST "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/<account_id>/magic/ipsec_tunnels?validate_only=true" \-H "X-Auth-Email: user@example.com" \-H "X-Auth-Key: XXXXXXXXXX" \-H "Content-Type: application/json" \--data '{"ipsec_tunnels":[{"name":"IPSec_cisco","customer_endpoint":"35.239.85.133","cloudflare_endpoint":"172.64.241.205","interface_address":"10.49.0.11/31","description":"Tunnel for Cisco 8000v"}]}'Create new IPSec tunnel
Request
curl -X POST "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/<account_id>/magic/ipsec_tunnels?validate_only=true" \-H "X-Auth-Email: user@example.com" \-H "X-Auth-Key: XXXXXXXXXX" \-H "Content-Type: application/json" \--data '{"ipsec_tunnels":[{"name":"IPSec_cisco","customer_endpoint":"35.239.85.133","cloudflare_endpoint":"172.64.241.205","interface_address":"10.49.0.11/31","description":"Tunnel for Cisco 8000v"}]}'Response
{"result": {"ipsec_tunnels": [{"id": "XXXXXXXXXX","interface_address": "10.49.0.11/31","created_on": "2022-05-03T23:03:19.104194Z","modified_on": "2022-05-03T23:03:19.104194Z","name": "IPsec_cisco","cloudflare_endpoint": "172.64.241.205","customer_endpoint": "35.239.85.133","description": "Tunnel for Cisco 8000v","health_check": {"enabled": true,"target": "35.239.85.133","type": "reply"}}]},"success": true,"errors": [],"messages": []}Generate Pre Shared Key (PSK) for Tunnel
Use the tunnel ID from the response in Step 2. Save the pre-shared key generated in this step as you will need it to set up tunnels on the Orchestrator.
Requestcurl -X POST "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/<account_id>/magic/ipsec_tunnels/<tunnel_id>/psk_generate?validate_only=true" \ -H "X-Auth-Email: user@example.com" \ -H "X-Auth-Key: XXXXXXXXXX" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json"
Response{
"result": {
"ipsec_id": "<ipsec_id>","ipsec_tunnel_id": "<tunnel_id>","psk": "XXXXXXXXXX","psk_metadata": {
"last_generated_on": "2022-05-06T17:37:03.70965667Z"
}
},"success": true,"errors": [],"messages": []
}
5. Define static routes
GRE tunnel configuration
Refer to Configure static routes for more information on configuring your static routes.
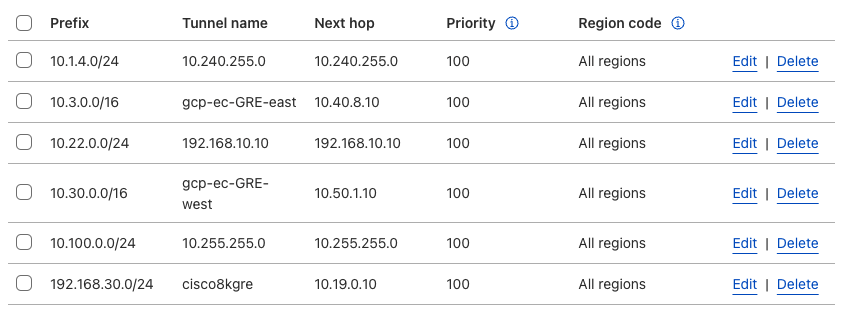
IPsec tunnel configuration
Define static routes on the 8000v router so Cloudflare can route traffic between sites.
For the purpose of the tutorial, create a route for the subnet 10.1.2.0/24 on the GCP branch to be routed via the established IPSec tunnel between the 8000v appliance and Cloudflare
Refer to Configure static routes for more information on configuring your static routes.
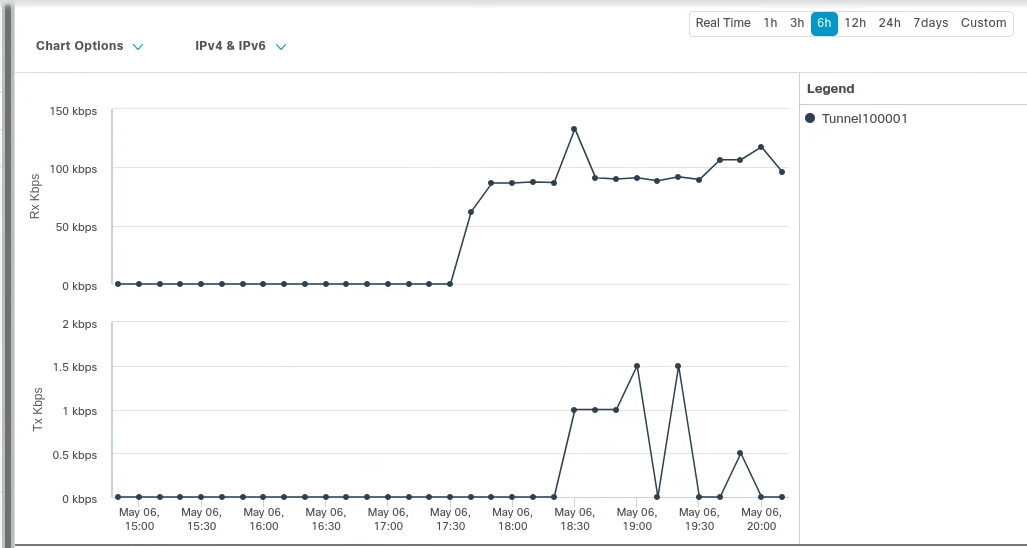
6. Validate traffic flow
GRE tunnel configuration
In the example below, a request for neverssl.com was issued, which has a Cloudflare policy blocking traffic to neverssl.com.
On the client VM (192.168.30.3), a blocked response is visible.
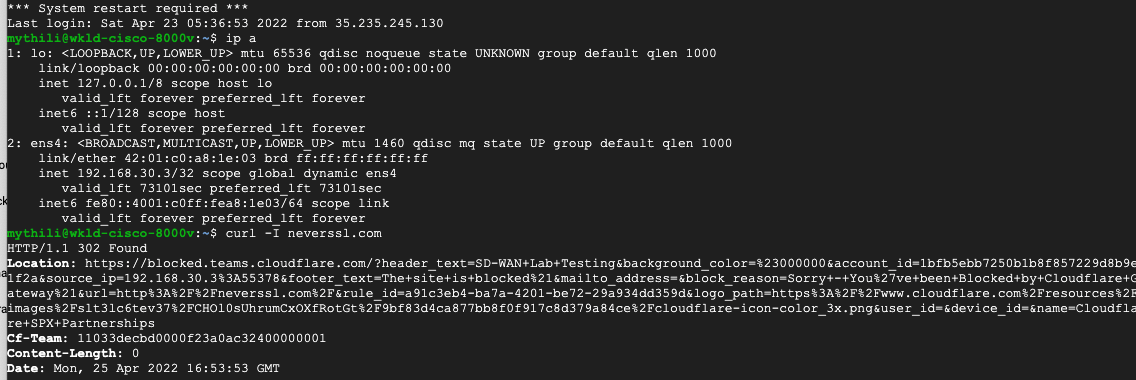
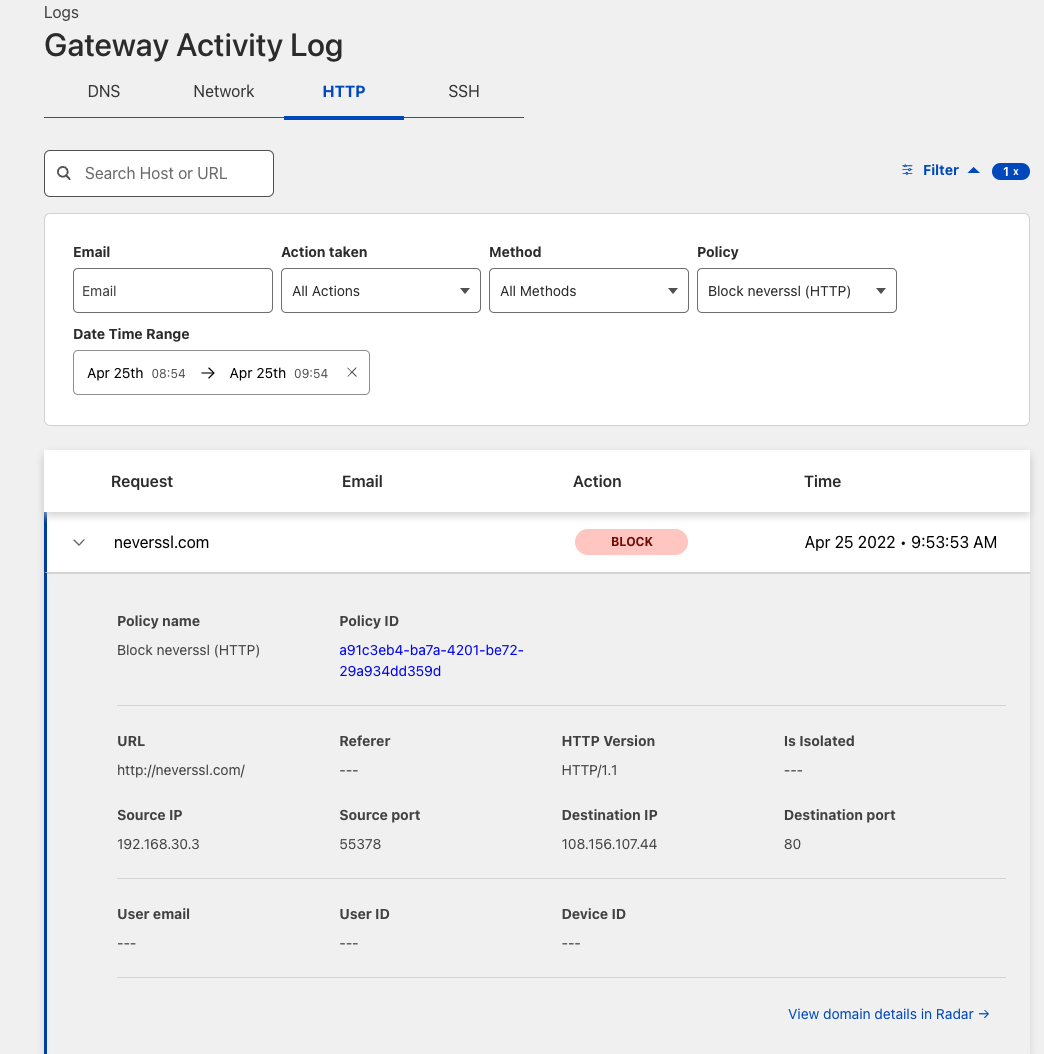
A matching blocked log line is visible from the Cloudflare logs.
Validate east-west traffic
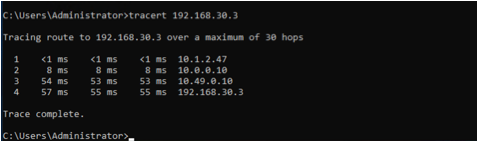
The example shows a client in AWS (10.1.2.23), which can ping the private IP of the router in GCP (192.168.30.3).
The traceroute shows the path going from the client (10.1.2.23)
→ to the AWS lan0 IP on the EdgeConnect (10.1.2.47)
→ to the Cloudflare private IPSec endpoint IP (10.0.0.10)
→ to the GCP private tunnel endpoint IP (10.49.0.10)
→ to the GCP workload (192.168.30.3).
This validates the east-west traffic flow through Cloudflare Magic WAN.
IPsec tunnel configuration
To validate traffic flow from the local subnet through Cloudflare’s Secure Web Gateway, perform a curl as shown in the example below.
On the client VM (192.168.30.3), a blocked response is visible.
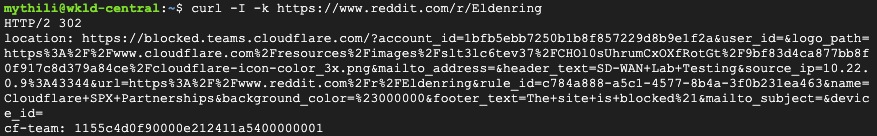
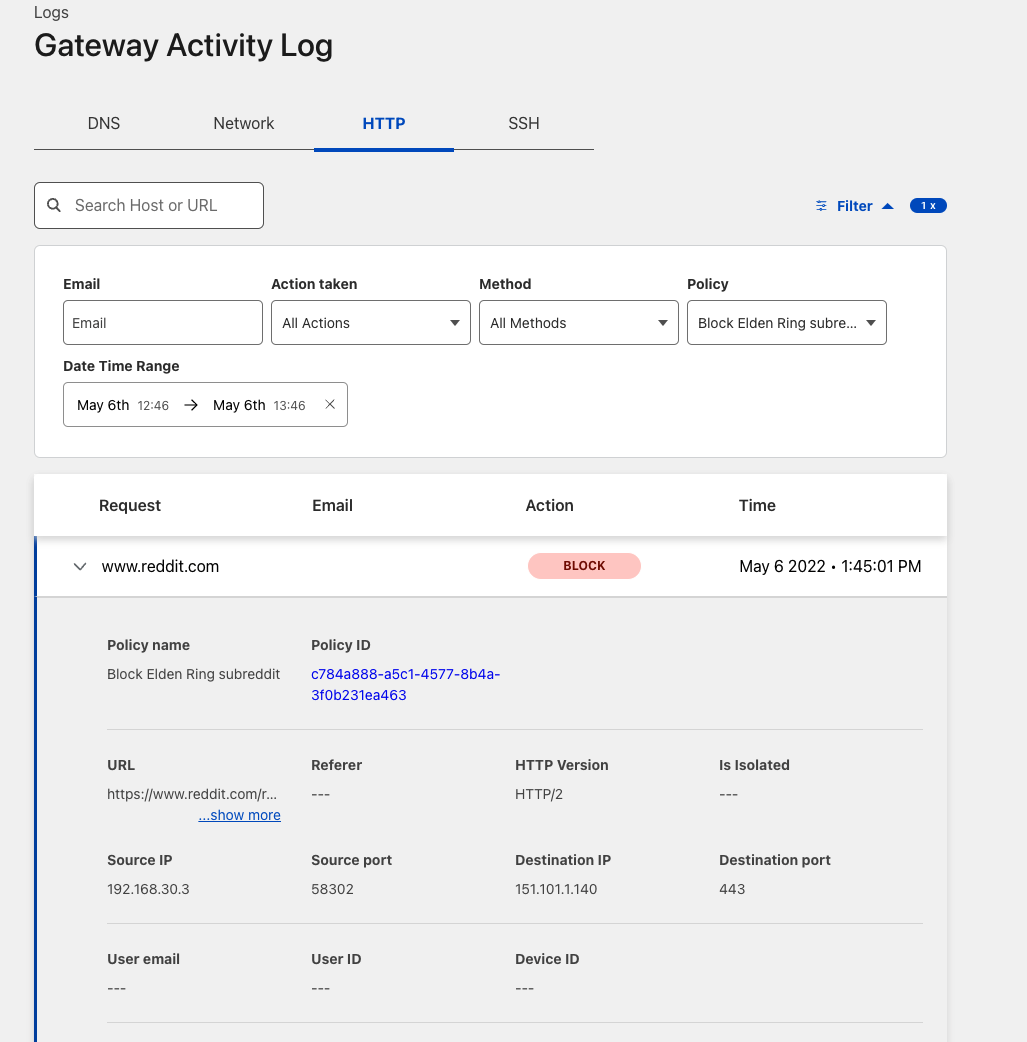
You can validate the request went through Gateway with the presence of the Cf-Team response header, or by looking at the logs in the dashboard under Logs > Gateway > HTTP.
You can also verify traffic flow through the established IPSec tunnel on the Cisco Device Dashboard > Interface.